Traverse Global v11.2 - Service Repair
Assigning ABC Codes Process
When the system assigns ABC codes, there are a number of ways it determines which code to assign to an item. This is based primarily on the value of the inventory item. Kitted and service items are not considered in this assessment; ABC codes are not assigned to kitted or service items.
When applying ABC codes to inventory items, the system takes a methodical approach to the process, determined by the settings established in the ABC Codes function combined with the options selected in the IN Assign ABC Codes function.
Notes:
- The Assign ABC Codes function does not assign ABC codes to kitted or service items, nor does it consider kitted or service items when determining which ABC code to assign to items.
- The Assign ABC Codes function uses current cost, not history cost, to calculate total value.
- When calculating value, the current cost is determined by the costing method selected in the IN costing method business rule. If the costing method is 'LIFO' or 'FIFO', the costing method from the IN zero costing method business rule is used.
- Mark the Include Obsolete Items check box if you want to include items with a status of 'Obsolete' in the Assign ABC Codes process.
ABC Codes
The first step is to set up ABC codes in the IN ABC Codes maintenance screen.
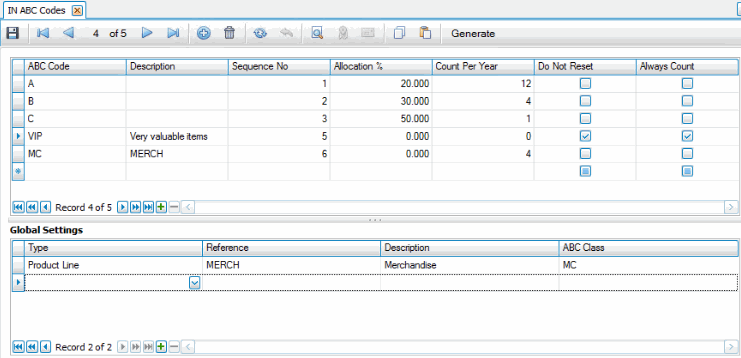
In the top section of the ABC Codes screen, you establish the sequence number and assign allocation percentage. This determines the items assigned to each ABC code:
| ABC Code | Sequence No | Allocation % | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 (highest value; counted most frequently) | 20 (Assigns the top 20% of total items to the code after being sorted by the value matching the criteria selected in the Assign ABC Codes function.) | Comprised of inventory that makes up 70-80% of your overall inventory value. |
| B | 2 (second highest value; counted second most frequently | 30 (Assigns the next 30% of total items to the code after being sorted by the value matching the criteria selected in the Assign ABC Codes function.) | Accounts for the next 10-15% of inventory value |
| C | 3 (third highest value; counted third most frequently) | 50 (Assigns the next 50% of total items to the code after being sorted by the value matching the criteria selected in the Assign ABC Codes function.) | Represents the bottom 10-15% of inventory value |
| Percent must total 100% |
- ABC Code: AKA 'ABC Class'. This code indicates which items you want to count more often vs. less often. Each item (except for kitted and service items) should have an ABC code (AKA ABC Class).
- Sequence No: This indicates the "level" of value to consider when assigning ABC codes. The lower the sequence number, the higher the value and the more often it will be counted. For example, if code A is sequence number 1, and the allocation % of code A is 20%, the items that make up the top 20% of the total value of all items will be assigned code A. If code B is sequence no 2 and the allocation % is 30%, the items that make up the next 30% of total value of all items will be assigned code B. And so on.
- Allocation %: Allocation of ABC codes is based on the total quantity of all items (except for kitted and service items). The allocation percentage indicates that the items that make up a percentage of the total items are assigned that code. An allocation of 20% means that 20% of the total items will be assigned that code. The sequence number determines which 20% of the total; the lower the sequence number, the higher the value. If seq. number 1 has an allocation of 20%, the code will be assigned to the 20% of items that make up the top total value. If seq. number 2 has an allocation of 30%, the code will be assigned to the 30% of items that make up the next total value.
- Count Per Year: This is the number of times in a calendar year that items assigned to this ABC code will be included in a cycle count batch. When the system selects items for a cycle count batch, it looks at all the items assigned to an ABC code, then divides that by the number of counts per year. For example, if you have 108 items assigned to ABC code 'B', and that code has a count per year of '12', nine of the items will be included in each of the 12 cycle counts, so that by the end of the year, all 108 items assigned to ABC code 'B' will have been counted.
The Count Per Year value, along with the Count Days Per Year value on the Cycle Count setup screen, determines how many items assigned to an ABC code will be counted every time a cycle count is performed. If Count Days Per Year is 24, and there are 108 items assigned to ABC code 'B' that has a count per year of 12, the calculation is as follows: (108 items * 12 counts per year)/24 count days per year = 54. This means 54 of the items will be included in each of the 24 cycle counts for the location, so that by the end of the year, all 108 items assigned to ABC code 'B' will have been counted 12 times.
- Do Not Reset: Every time the Assign ABC Code function is run, changes in total on-hand value, usage, or allocation percentages may change the ABC code assigned to an item. If you have items for which you want the ABC code to remain the same regardless of when or how many times the Assign ABC Codes function is run, mark the Do Not Reset check box: items assigned that ABC code will retain that code until you manually change it or clear the check box.
- Always Count: This indicates every cycle count batch will include the items with this ABC code.
Global Settings (optional)
In the bottom section of the ABC Codes screen, you can assign an ABC code to a group of items that belong to a particular product line, sales category, or account code. For instance, you might have office consumables you want may not want to include in cycle counts at all. You can create an ABC code and mark the 'Do Not Reset' check box in the top section of the screen. In the Global Settings section, you can then assign all items that have a product line of 'OSUPP' (Office Supplies) to that ABC code.
You can set up multiple global settings. However, if an item meets the criteria of more than one setting, the system will use the first setting to assign the code.
Assign ABC Codes
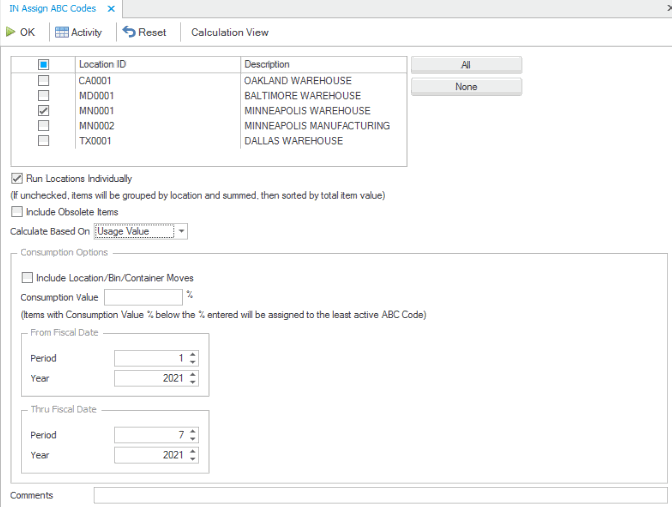
To determine which ABC code is assigned to an item:
- Ignore the ABC class for all items that have a Do Not Reset flag associated with the class (code). If the Do Not Reset check box is marked for an ABC code, then every item assigned to that ABC code will not be affected by the Assign ABC Codes function; the ABC codes for those items are not changed.
- Assign ABC codes based on Global Settings (the ABC class from the first ABC global setting that matches item/location).
- Assign ABC codes based on Consumption Value % (if calculating based on Usage Value or Usage Frequency)
- Assign ABC codes to all remaining items based on sequence number and allocation %.
ABC Code assignment example
Initial Scenario:
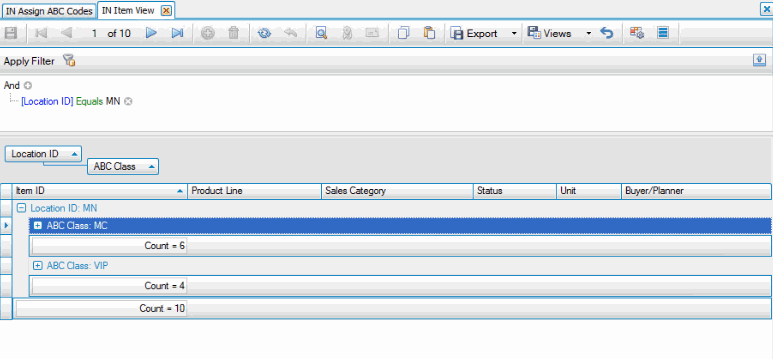
In IN location 'MN', 4 items are assigned to ABC code 'VIP'. There are an additional 6 items that are assigned to the 'MERCH' product line.
We have not run the Assign ABC code function.
The Item View interactive view shows the number of items assigned to each ABC class.
On the ABC Codes maintenance screen, the codes and global settings are set up:
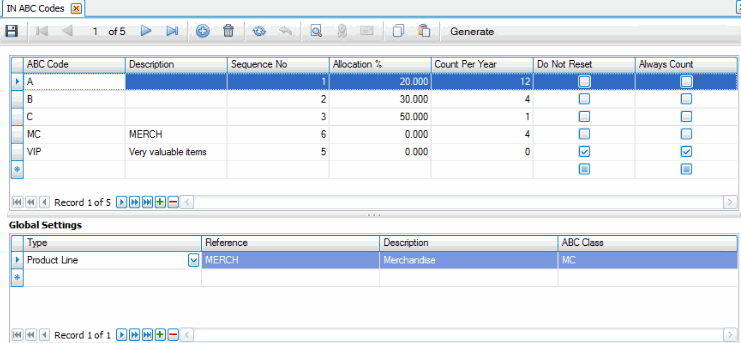
Notice the 'VIP' code is marked 'Do Not Reset' and 'Always Count'. This means that no matter how many times the Assign ABC Code function is run, the items with the 'VIP' ABC code will never change. Also notice the 'VIP' code is marked to 'Always Count'; these items will be included in every cycle count batch.
Note: In our example, the total number of items to be assigned an ABC code in the MN location is 132.
Run the Assign ABC Codes function set to calculate based on 'On Hand Value'.
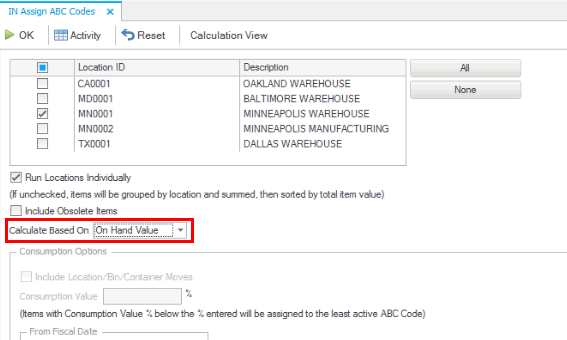
First, the system ignores the ABC class for all items that have a Do Not Reset flag associated with the class (code). The 'VIP' ABC code is marked as 'Do Not Reset'. There are 4 items that are assigned to the 'VIP' code. These items can be removed from the total number of items considered for ABC codes because that code will never change. In our example, this leaves 128 items to have an ABC code assignment (132 - 4 = 128)
Next, the system assigns codes based on the global settings from the ABC Codes maintenance screen. According to the global settings, any item with a product line = 'MERCH' should be assigned to the 'MC' ABC code. In our selected location (MN) there are 6 items that belong to the 'MERCH' product line, so those will always be assigned to the 'MC' code.
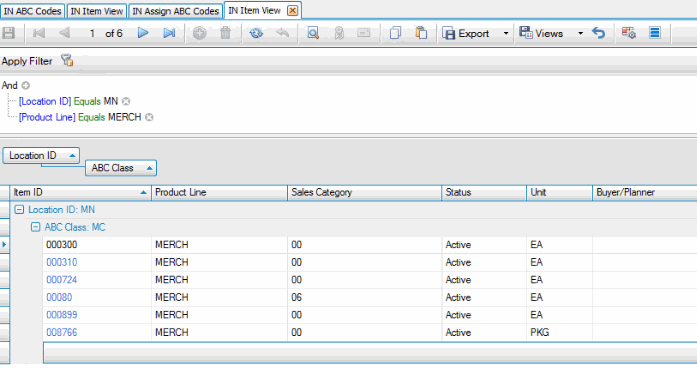
In our example, this leaves 122 items to be assigned an ABC code (128 - 6 = 122).
We are not assigning ABC codes calculated based on 'Usage Value' or 'Usage Frequency', so the system will skip the consumption options.
The system will then assign ABC codes to all remaining items based on sequence number and allocation %. Because we are assigning ABC codes calculated based on the on-hand value, the system will evaluate the total inventory value of the remaining 122 using the costing method selected in the IN business rule. Note: You must have updated costs in Item maintenance to get accurate values.

The system will use the total on-hand quantity and the costing method to find the total quantity ranked by on-hand value (highest on-hand value to lowest on-hand value). The items assigned to each code is determined by the sequence number and the allocation percentage.
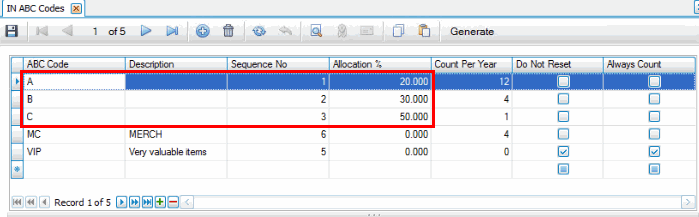
The lower the sequence number, the higher the value for the allocation %.
According to the ABC Codes maintenance screen in our example, the top 20% (sequence number = 1) of items in the ranked total will be assigned to ABC code 'A'. The next 30% of items in the ranked total will be assigned to code 'B'. The next 50% of items (remaining items) will be assigned to code 'C'.
We can verify the system assigned codes following these allocation percentages by looking at the quantity of items:
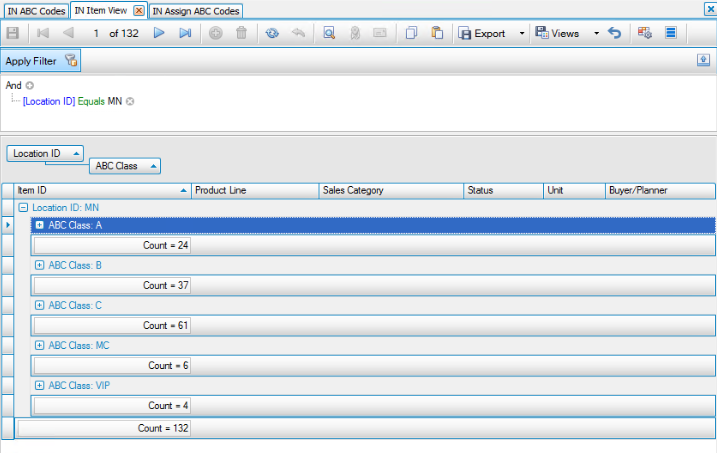
Out of a total of 122 items:
- 20% should have ABC code 'A'. 20% of 122 is about 24.
- 30% should have ABC code 'B'. 30% of 122 is about 37.
- 50% should have ABC code 'C'. 50% of 122 is about 61.
Run the Assign ABC Codes function set to calculate based on 'Usage Value'. Do not include location/bin/container moves. Do not enter a consumption value.
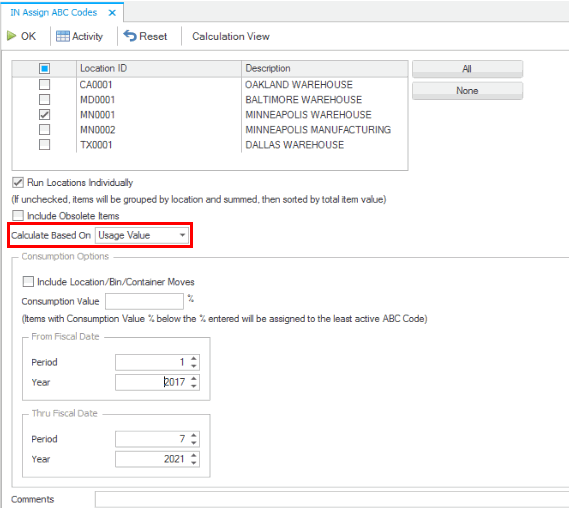
First, the system ignores the ABC class for all items that have a Do Not Reset flag associated with the class (code). The 'VIP' ABC code is marked as 'Do Not Reset'. There are 4 items that are assigned to the 'VIP' code. These items can be removed from the total number of items considered for ABC codes because that code will never change. In our example, this leaves 128 items to have an ABC code assignment (132 - 4 = 128)
Next, the system assigns codes based on the global settings from the ABC Codes maintenance screen. According to the global settings, any item with a product line = 'MERCH' should be assigned to the 'MC' ABC code. In our selected location (MN) there are 6 items that belong to the 'MERCH' product line, so those will always be assigned to the 'MC' code.

In our example, this leaves 122 items to be assigned an ABC code (128 - 6 = 122).
We are assigning ABC codes calculated based on 'Usage Value' with a time frame selected. Usage indicates consumption. and looks at transaction history within the specified period of time. The transaction types considered for consumption include Material Requisitions, MP Build Component, AR Invoice, SO Verify, SO Invoice, IN Verify, IN Invoice Sale, BM Build Component, BM Unbuild Assembly, WM Material Requisitions. When you include location/bin/container moves, the transaction types also include Transfer From, WM Transfer From, and Move Out.
When calculating based on usage value, the system evaluates usage value at the current cost (not history cost) to determine the total value, and will rank items accordingly.
The system will then assign ABC codes to all remaining items based on sequence number and allocation %. The system will evaluate the total usage value of the remaining 122 using the costing method selected in the IN business rule. Note: You must have updated costs in Item maintenance to get accurate values.
The system will use the total consumed quantity within the period selected and the current cost (per the costing method) to find the total quantity ranked by usage value (highest consumed value to lowest consumed value). The items assigned to each code is determined by the sequence number and the allocation percentage.

The lower the sequence number, the higher the value for the allocation %.
According to the ABC Codes maintenance screen in our example, the top 20% (sequence number = 1) of items in the ranked total will be assigned to ABC code 'A'. The next 30% of items in the ranked total will be assigned to code 'B'. The next 50% of items (remaining items) will be assigned to code 'C'.
We can verify the system assigned codes following these allocation percentages by looking at the quantity of items:

Out of a total of 122 items:
- 20% should have ABC code 'A'. 20% of 122 is about 24.
- 30% should have ABC code 'B'. 30% of 122 is about 37.
- 50% should have ABC code 'C'. 50% of 122 is about 61.
However, the items assigned to each code may be different than those assigned to a code calculated by on-hand value. The Assign ABC Codes log shows the changes.
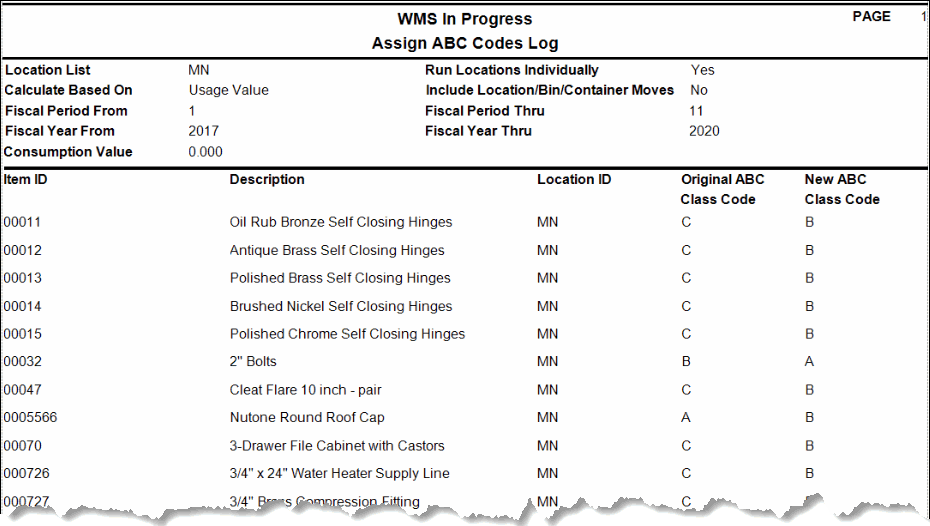
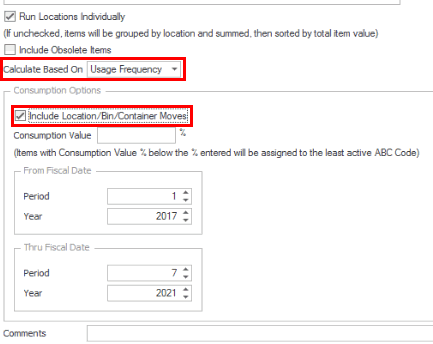
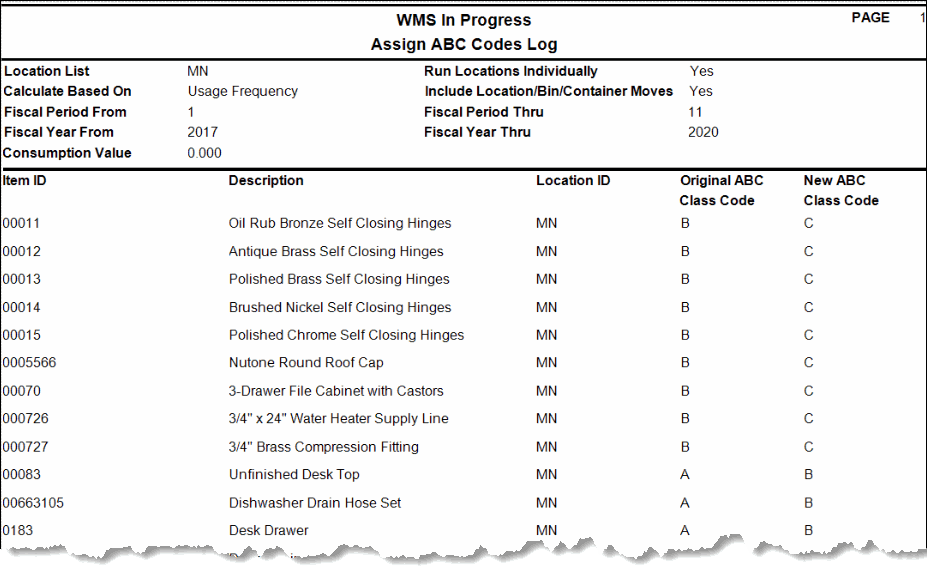
If we run the Assign ABC Codes function again with the Include Location/Bin/Container check box marked, the assigned ABC codes may be different again because there are additional transactions considered (Transfer From, WM Transfer From, Move Out (WM Move Quantities)) when determining usage.
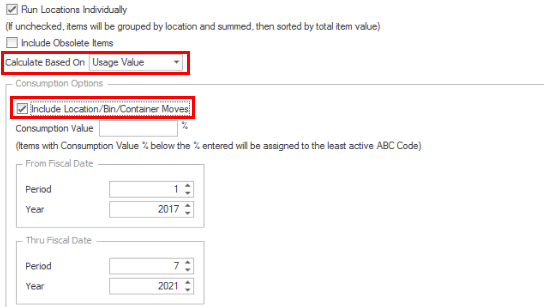
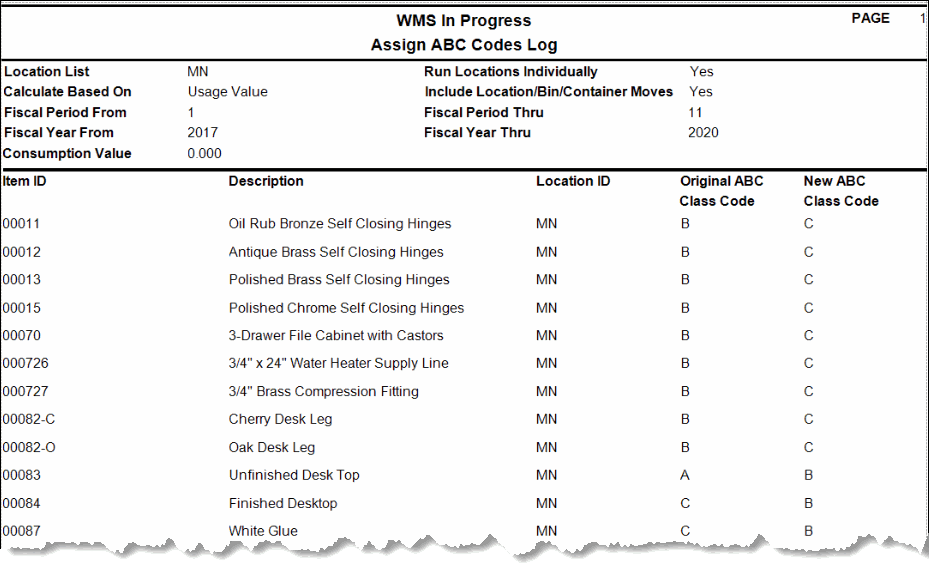
Consumption Value
The consumption value is useful for items that you might use often but are so inexpensive they may have essentially no value. You may want to assign the least-active ABC code to those items.
When you enter a Consumption Value percentage, all items with a total value percentage less than the consumption value percentage are assigned to the least-active ABC code.
Run the Assign ABC Codes function set to calculate based on 'Usage Frequency'. Do not include location/bin/container moves. Do not enter a consumption value.
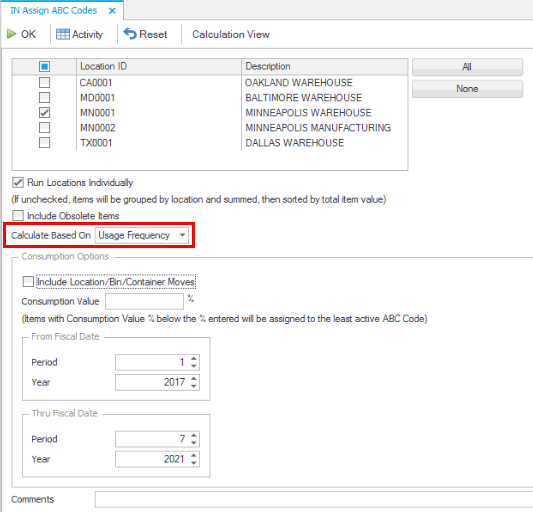
First, the system ignores the ABC class for all items that have a Do Not Reset flag associated with the class (code). The 'VIP' ABC code is marked as 'Do Not Reset'. There are 4 items that are assigned to the 'VIP' code. These items can be removed from the total number of items considered for ABC codes because that code will never change. In our example, this leaves 128 items to have an ABC code assignment (132 - 4 = 128)
Next, the system assigns codes based on the global settings from the ABC Codes maintenance screen. According to the global settings, any item with a product line = 'MERCH' should be assigned to the 'MC' ABC code. In our selected location (MN) there are 6 items that belong to the 'MERCH' product line, so those will always be assigned to the 'MC' code.

In our example, this leaves 122 items to be assigned an ABC code (128 - 6 = 122).
We are assigning ABC codes calculated based on 'Usage Frequency' with a time frame selected. Usage indicates consumption. Usage frequency looks at transaction history in the specified period of time. The transaction types considered for consumption include Material Requisitions, MP Build Component, AR Invoice, SO Verify, SO Invoice, IN Verify, IN Invoice Sale, BM Build Component, BM Unbuild Assembly, WM Material Requisitions. When you include location/bin/container moves, the transaction types also include Transfer From, WM Transfer From, and Move Out.
When calculating based on usage frequency, the system evaluates usage frequency as the total number of consumption-type transactions for items in the time period, and will rank items accordingly.
The system will then assign ABC codes to all remaining items based on sequence number and allocation %.
The system will use the total consumed quantity within the period selected to find the total quantity ranked by usage frequency (highest transactional frequency to lowest transactional frequency). The items assigned to each code is determined by the sequence number and the allocation percentage.

The lower the sequence number, the higher the frequency for the allocation %.
According to the ABC Codes maintenance screen in our example, the top 20% (sequence number = 1) of items in the ranked total will be assigned to ABC code 'A'. The next 30% of items in the ranked total will be assigned to code 'B'. The next 50% of items (remaining items) will be assigned to code 'C'.
We can verify the system assigned codes following these allocation percentages by looking at the quantity of items:

Out of a total of 122 items:
- 20% should have ABC code 'A'. 20% of 122 is about 24.
- 30% should have ABC code 'B'. 30% of 122 is about 37.
- 50% should have ABC code 'C'. 50% of 122 is about 61.
However, the items assigned to each code may be different than those assigned to a code calculated by usage value. The Assign ABC Codes log shows the changes.
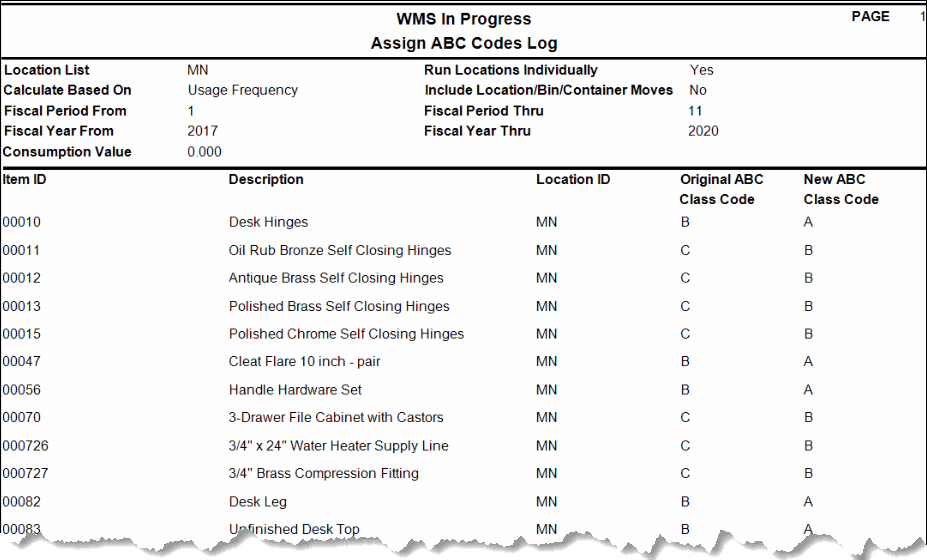
If we run the Assign ABC Codes function again with the Include Location/Bin/Container check box marked, the assigned ABC codes may be different again, because there are additional transactions considered (Transfer From, WM Transfer From, Move Out (WM Move Quantities)) when determining usage.
Consumption Value
The consumption value is useful for items that you might use frequently but are so inexpensive they may have essentially no value. You may want to assign the least-active ABC code to those items.
When you enter a Consumption Value percentage, all items with a total frequency percentage less than the consumption value percentage are assigned to the least-active ABC code.